Know Your Electricity Bill-Understanding Complete Detail
Most people feel that it is a difficult task to understand the electricity bill. I don’t think. I hope after this article you will be able to know your electricity bill completely.
Table of Contents
How to Know Your Electricity Bill:
To know your electricity bill we need to know the important terminology used. Such as fixed charge, unit, load, Maximum demand, etc.
Don’t worry we will cover all the terminology so that you can easily understand the electricity bill. First of all, there is an image below in which I have highlighted the important term. We will understand all the terms one by one which will help you to know your electricity bill.
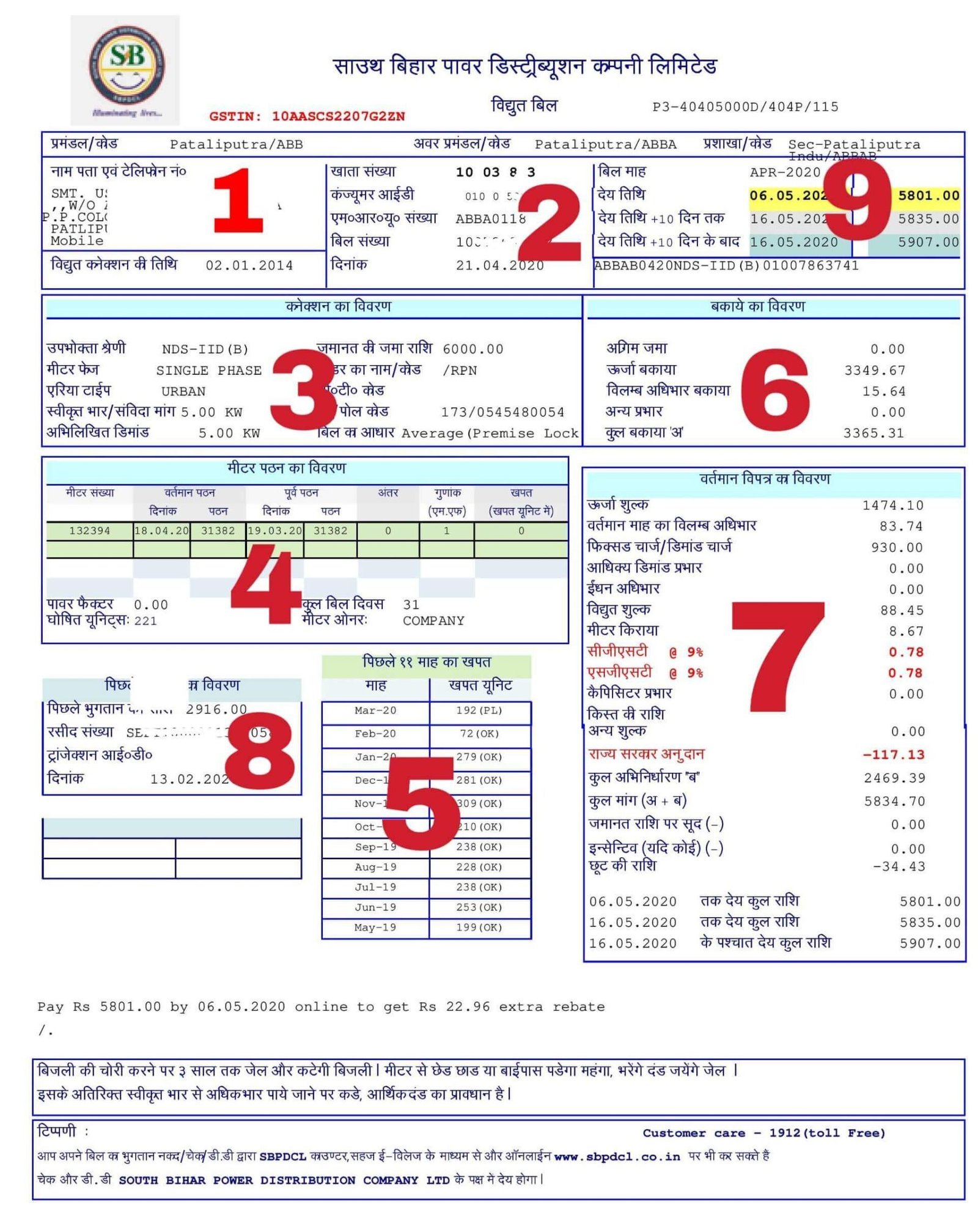
To understand the bill easily, I have divided the bill into nine parts. Now we will discuss each part and we note the important words for that part. Then we will also discuss that important word one by one.
All Components of an Electricity Bill
1. Name and Address :
It is only showing the name and address of the consumer. Or you can call it the name and address of the power connection holder. There is nothing to note here.
2.Consumer ID or CA Number:
In this section, you will find a unique number which is named “खाता संख्या “. It is also called the account number or consumer number of your bill. It is a unique number provided by the service provider. Sometimes it is also called the CA number or contract account number. It is your identity to the service provider or electricity company. Through this ID you can check your electricity bill details or pay online.
3.Electricity Connection Details:
It is the most important section of the bill. Here you will find the technical details of your electricity connection. Here you can see the first line “उपभोक्ता श्रेणी “. It shows the category or type of connection. It is also called rate category or simply tariff or only category.
Second-line shows the phase of the connection whether it is single-phase or three-phase. In the image, it shows it is a single-phase electricity connection.
The third line is your area type whether it is urban or rural.
The fourth line is “स्वीकृत भार /संविदा मांग “. That is Sanctioned load.
The fifth line is “अभिलिखित डिमांड “. That is Recorded demand.
In this part there four important terminologies which are to be noted. These are
1. Tariff/Rate Category
2. Phase
3. Sanctioned Load
4. Recorded demand or Maximum demand
All the above four terminologies are very important to understand the electricity bill. We will discuss all these terminologies in detail later in this article.
4.Meter Reading Detail:
This section shows the meter reading details of your meter. You can see current meter readings and previous readings here. In the above image, both readings are the same. Because the reading has not been taken by the meter reader hence the bill is issued on an average basis. I will discuss it later in the article.
5.Previous Consumption Details:
In this section, you can see the previous 11-month consumption details. This also shows your consumption pattern that what was your consumption in summer and what was in winter.
6.Arrear Details:
Here you can see the arrear of your electricity bill. If you have not paid your previous electricity bill. Then here you can find the total due amount from the previous bills. It will show zero amount if you pay your bill regularly. It may be negative if you have paid some extra amount.
7.Details of Your Current Bill:
This is a complete description of your current bill. It shows the calculation of your current electricity charges including energy charges, fixed charges, delay payment surcharge (DPS), meter rent, etc. We will also discuss the entire calculation.
8.Last Payment Detail:
Here you can see your last payment details. It shows your last payment amount, date, and receipt number. you can verify it from your last payment receipt. If here it does not shows your last payment details then it may be that your last payment is not adjusted in your bill. In that case, you should contact your nearest utility office or you can complain to toll-free number 1912.
9.Due Date of Electricity bill:
In this section, you can see the month and year of the bill. The above image shows the billing month as April-2020. After that, it shows the due date. The due date is generally 15 days from the date of billing. If you pay your bill within the due date you get some rebate on your bill amount.
So now we have covered all the sections of the bill. But still, we have not discussed all terminologies of the bill. To know your electricity bill it is very important to understand these terminologies. So here I have collected all the terminology and points, which we will now discuss one by one.
Here is a list of all the components of the electricity bill which are very important and we are going to discuss.
Important Terminologies to Understand the Electricity Bill
- Tariff/Rate Category
- Sanctioned Load
- Recorded Demand/Maximum Demand
- Bill Basis
- Unit Rate Slab Structure
- Energy Charge
- Fixed Charge
- Excess Demand Charge/Maximum Demand Penalty
- Delay Payment Surcharge(DPS)
- Meter Rent
- Electricity Duty
- Calculation of Electricity Bill
Tariff/Rate Category :
There are many different types of power connections. The type or category is called the tariff. All the categories have different rates. I mean the unit rate of electricity differs in a different category. This classification is done on a different basis.
According to the supply voltage, it is divided into two-part, LT(Low Tension) and HT(High Tension).

LT(Low Tension)-230V/400V:
Now the LT is divided into two-part single-phase and three-phase. Supply voltage in single-phase is 230Volts and 400Volts in three-phase. These single-phase and three-phase connections are used in our home, shop, and at different places.
These single-phase and three-phase connections are used in our home, shop, and at different places.
HT(High Tension)- 11kV/33kV/132kV/400kV:
HT connections are used by big consumers who need the bulk power supply. Such as Malls, Big Hospitals, Industries, etc. They need bulk power supply so they need supply at higher voltages, that is HT connection. Supply voltage in HT connection is generally 11kV(11 kiloVolts), 33kV, 132kV or above.
Now the above three categories are divided into different categories according to the purpose of connection. Such as if you need an electricity connection for domestic use there is a different category and have a different rate. If you need an electricity connection for commercial purposes there is a different category and hence their rate is different.
So, according to the purpose of electricity connection, it is further divided as Domestic, Commercial, Industrial, Agricultural, etc.
So as per our need, we get an electricity connection.
In our sample image of the bill, you can see the “उपभोक्ता श्रेणी ” as NDS-II in section 3. That is it is a commercial connection. Here NDS represents Non-Domestic Service. NDS is just a nomenclature for commercial connections. Similarly, the nomenclature for domestic connection is DS for industrial LTIS in Bihar. These nomenclatures may vary in a different states. For more details, you can watch this video.
Sanctioned Load:
The sanctioned load is also called the connected load. Every electricity connection has an allowed load to use, which is called the sanctioned load. You might have heard that my electricity connection is 5kW, 2kW, 7kW, etc. Actually, it is the allowed load of that connection that is the sanctioned load of the connection.
In our sample image of the bill, you can see the “स्वीकृत भार /संविदा मांग ” as 5kW. This means that the sanctioned load of the connection is 5kW. If the connection holder uses a load of more than 5kW, he will have to pay a fine.
Recorded Demand/Maximum Demand:
Recorded demand is the actual load used by the consumer. Whatever we use in our home, shop or industry, their load is measured by the meter. And the meter records the maximum load. The maximum load recorded by the meter is called the recorded demand.
For Example, Suppose you are using 10 fans having a load of 500 watts, an AC having load of 1500 Watts, 10 tube lights having a load of 400 watts. Then the meter records the maximum load as 2400 Watts that is 2.4kW. It is the recorded demand. In case two days later if you will use some extra load that is 2.5kW then now the meter will keep your recorded demand as 2.5kW. It will erase the old lower demand recorded earlier. In simple, you can say that the meter keeps the record of the maximum load used by the consumer at a time. That is why it is also called maximum demand.
In our sample image of the bill, you can see the “अभिलिखित डिमांड ” as 5kW in section-3. This means that the recorded demand is 5kW. If the connection holder uses a load of more than 5kW, he will have to pay a fine because the sanctioned load is also 5kW.
Most of the people get confused about recorded demand, sanctioned load, and maximum demand. I hope you understand the point. It will help you to understand the bill.
Bill Basis:
The electricity bill can be issued on an actual basis or on an average basis. When the meter reader takes the meter reading and issues a bill based on your actual consumption it is called the actual basis. But for some reason, if the meter reading is not done many times, then the electricity company issues the bill on an average basis. It is called the average basis.
Issuing a bill on the actual basis is an ideal case. But average bills are issued for several reasons.
In our sample image of the bill, you can see the “बिल का आधार ” as Average(Premises Lock) in section-3. It means that the above bill is issued on an average basis due to premises lock.
Average bills are issued mainly for two reasons. First premises lock and the second is meter defective. Here I am writing some words which are used to indicate the basis of the bill and what are their meaning.
Actual Bill Basis:
The Symbols used to indicate the actual bill basis are:
- Actual
- OK
- Normal etc…
Average Bill Basis:
The Symbols used to indicate the average bill basis are:
- MD (meter defective): It shows that the bill is issued on an average basis because your meter is defective.
- IDF (Identified defective): It indicates that your meter is identified as defective hence average bill issued.
- RDF (Reading defective): It shows that your meter reading taken by the meter reader is not in a progressive manner or it is wrong. and hence an average bill issued.
- ADF (Appears defective): When the meter reader enters the same reading as the previous meter reading then the billing software detects the meter as defective. Hence it issues an average bill.
The above terminologies are very important to know your electricity bill in detail. Otherwise, you may get confused about your bill.
Unit Rate Slab Structure:
It is very important to know your electricity bill calculation.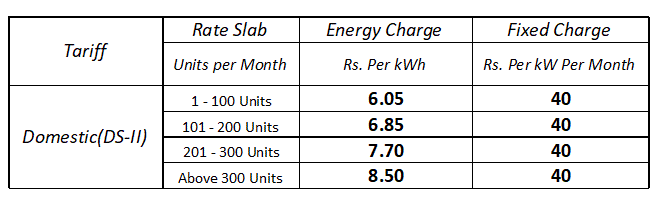
From the above table here, you can understand that the unit rate is not the same for every unit. When consumption is increasing the unit rate is also increasing. This type of unit slab rate rewards low-energy users and promotes others to save electricity. Sometimes fixed charges also increase with the increase in consumption. Here you can check out the unit rate structure of Bihar.
Energy Charge/Unit Charge:
In our sample electricity bill, you can see the “ऊर्जा शुल्क ” in section -7. It is actually the unit charge or energy charge. It totally depends on your unit consumption. If your consumption falls to zero in a month, then this energy charge will be zero for that month. In some cases, it will not be zero if the minimum monthly charge(MMC) is applicable.
Fixed Charge:
The fixed charge is a part of the electricity bill charges. Generally, it is independent of energy consumption. It depends upon the sanctioned load or maximum demand. In the above image of the unit structure, you can see the fixed charge as Rs. 40/kW/Month. It depends only on the load of the connection that is usually fixed. Therefore the fixed charge remains fixed as long as the consumer does not use more load than the allowed load.
As I said it is independent of your energy consumption, it means that you will be charged even if you consume zero units. You will better understand when we will calculate the electricity bill.
Excess Demand Charge/Maximum Demand Penalty :
The excess demand charge is a type of penalty. If a consumer usage the total load higher than the sanctioned load, He is liable to pay the excess demand charge. Suppose a consumer having sanctioned load is 5 kW. But he is using the total load of 7kW. Then for his extra load of 2kW, There will be a penalty in his bill called excess demand charge.
Delay Payment Surcharge(DPS):
It is the late fine of your bill. As its name suggests it is a surcharge for the delay in bill payment.
Meter Rent:
Meter rent is a self-explanatory term. Usually, the meter is provided by the electricity company, so they charge the meter rent.
Electricity Duty:
Electricity duty is a type of tax. In some states, it is zero but in some states, it is not.
How to Calculate the Electricity Bill:
To understand the calculation of the electricity bill we will take an actual example of a bill. 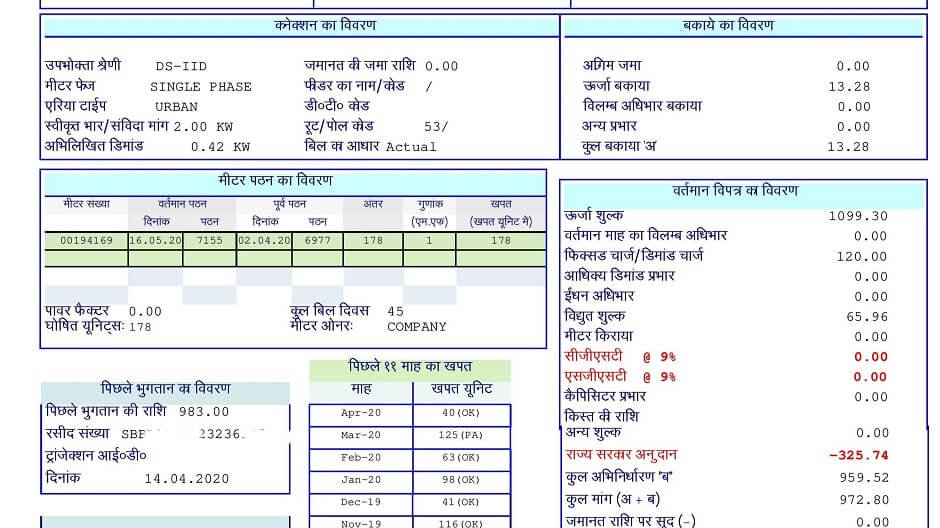
Now we will calculate the above electricity bill.
Here the unit consumption is 178 units for 45 days. and the connection is domestic DS-IID. The tariff rate of DS-II is as below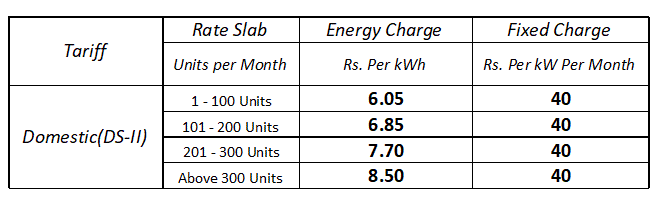
Here the unit rate is given for monthly consumption. So first of all, we will find out the consumption for one month that is 30days.
So, the consumption for 30 days =(178/45)*30 = 118.667 Units
Now the Energy charge for 118.667 Units is as below:
for 1-100 Units: 100×6.05= 605/-
for 101-118.667 Units: 18.667×6.85=127.87/-
That is a total= 605+127.87= 732.87/- (It is the unit charge of 118.667 Units or for 30 days).
Now the total unit charge for 178 units for 45 days = (732.87/30)x45 =1099.30/-(you can match with the bill)
Fixed charge = load x fixed charge rate= 2×40=80(for 30days).
Since the bill is for 45 days, the Total fixed charge=120/-
Here Excess demand charge is zero because recorded demand is less than sanctioned load.
In Bihar, electricity duty is charged @6% of the energy charge. So,
Electricity duty = 1099.3 x 6%=65.96/-
In Bihar, the meter rent is removed from the tariff so it is zero.
Here capacitor charge is also zero because the power factor is not measured in the bill.
Now the Government subsidy @ Rs.-1.83/Unit = 325.74/–
So, The total bill=1099.3+120+0+65.96+0-325.74 = 959.52/-
Strategy to know Your Electricity Bill:
To know your electricity bill you have to understand all components of the electricity bill and its charges. Then you can understand easily. It is nothing but simple mathematics and some terminologies.
I hope you liked the article. If you have any doubts or suggestions please comment below and share with your friends. It will help me a lot. Thank you.
Also read: What is 1 Unit of Electricity, Power Consumption kWh and Wattage kW?


A nice explanation even a person not having electricity knowledge can understand.thanks a lot for making bill reading so easy.
Well explained.thankyou for this .As i could understand about electricity billing very easily.
You should also explain “excess demand charge” with example, where there was excess demand greater than zero.
its really good know about electricity bill and thank you so much because this blog is very informative and easy to understand
Dear Sir,
I increased load 1 year before at mohali punjab, since we are receiving a high bill. Most of the time they send average bill. 50k or 70 k.
This time one person came as je and told you have a printing press and you came under Non commercial but on your bill written MS MS category – you pay me 90k cash otherwise you will face problems.
Next day he send a bill 7.28 lac, when we gone office, SDO told no need to give complaint we will rectify, but after 3 days he said one new objection raised. We are fed up since 11 months. Last Bills amounts are beyond our capacity. Plz suggest us we are ready to pay your consultation.